What Is The Use of CT Scan For Root Canal?
Did you know a CT scan for a root canal can help with better endodontic diagnostics and treatments? Today’s contemporary endodontic treatments have changed some of the traditional practices of dentistry. The advancements of new equipment like the cone-beam computed tomography (CBCT) are changing how an endodontist determines a patient’s root canal condition and treatment. CT scan produces an accurate high quality detailed 3D X-ray image. The images deliver incredible features of the tooth’s structure. The x-rays consist of the surrounding tissue conditions as well as the jaw’s bone structure.
Table of Contents
What is a CT scan for teeth?
CBCT was approved by the Food and Drug Administration in 2001. The beam’s rotating technique captures the surrounding and middle areas of the tooth. It’s helping to determine the exact treatment needed for the tooth’s condition. CBCT captures cross-sectional images. The technology provides views of the soft tissue, bone, and blood vessels. Traditional imaging techniques have been limited to the detailing they provide. Medical practices use both CT to view bone structures combined with MRI to see blood vessels and soft tissue. CBCT has combined both of these viewing forms to display the tooth’s physical traits. The 3D X-ray is making it easier for practitioners to detect problems. And based on the diagnostics a more effective treatment is being prescribed. The goal is to ensure healing in the short and long-term root canal treatments.
CBCT is a faster and safer version of the regular x-ray. The use of a cone-shaped X-ray beam reduces the time needed for scanning. A full scan takes under one minute. The radiation dose is one hundred times less compared to a regular scanner. Oral health professionals still rely on multiple 2-D imaging for diagnosis and treatment planning. 3-D scans now offer practitioners the ability to collect much more data with a single scan. Studies confirm the radiation dose, and exposure to endodontic treatments is extremely low with little to no risk.
The cone-beam computed tomography provides practitioners with a full view of the tooth’s condition. 3D X-ray also captures less distinct dental conditions contributing to the patient’s oral health. Canals that were left untreated by previous practitioners may have been concealed causing root canal infections. Teeth or structures outside of the endodontic field of practice may also need attention. For this reason, the 3-D X-ray detail is so inclusive the images can be shared with other practitioners. It’ reduces the need for the patient to undergo multiple scans for each practitioner. That’s a cost-saving for the patient and less exposure to radiation. More important, the collaborations provide accurate information about past and current dental care. It’s a better method of monitoring treatment results. It also provides accurate re-treatment scheduling when needed.
Why would a dentist do a CT scan?
3D technology allows root canal diagnostics and treatments to be done in the office. In some cases, this new technology is eliminating the need for exploratory surgery. The benefits for the patients are accurate diagnoses. The accuracy can reduce the number of required visits for treatment and follow-ups. Depending on the conditions and the potential future outcomes non-surgical treatment planning may be recommended. The added value of advanced technology is the precision of diagnoses. And the patients see a higher rate of improved dental health with less pain.
Will a CT scan show a tooth infection?
Today’s 3D X-ray is critical in determining the proper treatment for the first time. And the details are aiding to foresee future conditions based on the tooth’s structure. For some patients with curved roots or complicated canals, extra precautions may be required to ensure proper treatment. The 3D picture has gone beyond the traditional x-ray process of the past. These images are helping to identify other conditions that may affect the healing process. These same terms may have changed or prevented previous root canal treatments from working. Some patients continue to have infections or problems even after proper root canal therapy. The 3D imagery may be able to determine the actual cause of the tooth failing to heal completely.
These pictures help to identify:
- canal perforations and broken instruments.
- existing problems with prior root canal treatments.
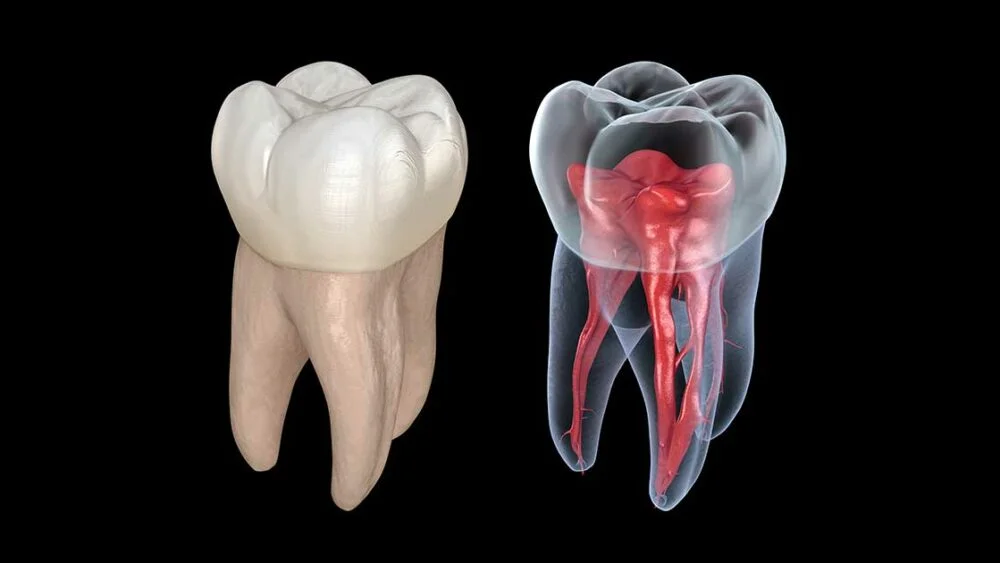
- Capturing the entire structure of each root including the nerve helps to eliminate any surprises for the treating endodontist.
- detecting the tooth’s current condition
- provides helpful insight into potential problems.
What are the Indications of 3D X-Ray?
Understand that by the time a root canal is necessary the tooth may already be beyond repair. But, rather than pull the tooth or placed an implant, a root canal can keep the tooth in place with a crown. The endodontist needs to make a diagnosis of whether or not a root canal will cure the condition. The examination determines if the pulp can recover or the tooth is dead. The CBCT 3D imagery allows the endodontist to view the infected tissue surrounding the root and within the canal. Based on the condition the endodontist will treat the infection or replace the tooth.
If the tooth can be saved, the endodontist removes the inflamed or infected pulp. By using the 3D X-ray, they can carefully maneuver the insides of the canal. Then it’s filled and sealed to prevent any further infection. If the tooth is to be replaced with an implant, a 3D X-ray is taken from the pre-implant bone area and nerves to make a full assessment. The image ensures the implant is placed at a safe distance from the arteries, veins, and nerves.
If nonsurgical retreatment is not an option, your endodontist may suggest surgery. This surgery involves making an incision to allow access to the tip of the root. The 3D scans help to avoid surprises during surgery. When dealing with the health of patients practitioners need as much information as possible. 3D X-rays contribute to revealing hidden structural conditions or unseen infections. These surrounding conditions could result in more severe health issues. For most patients experiencing ongoing root problems, these unknown issues are usually the cause.
How A CT Scan for Root Canal Can Be Used In Dental Treatment Complications?
Case studies show CBCT scans can detect root canal complications. The condition may have been missed using the traditional x-ray methods. This technology is highly recommended for the detection of early resorption. In dentistry, the term resorption refers to changes to the tooth’s root. The changes are not always due to decay or fracture. These changes occur in the external or internal parts of the tooth. The internal condition affects the root of the pulp space of the tooth. External resorption changes have to do with the outside of the tooth surface. This is where the tooth’s root connects to the jawbone. Completely avoiding either of the following conditions may result in the loss of the tooth.
- A curved or narrow canal was not treated properly
- Complicated canals have multiple nerve branches within the canal
February 15, 2023What Is The Average Cost Of Braces In Houston?
February 01, 2023What You Need to Know About Dental Hygienists?
January 30, 2023What to Expect During the Wisdom Teeth Extraction
October 23, 2022Wisdom Tooth Removal Cost
October 23, 2022Dental Emergency, Open Saturday
October 23, 2022Full Guide to Dental Crown
July 26, 2022Should I Have My Wisdom Teeth Removed Before I Get Braces?
July 26, 2022Complete Guide to Wisdom Tooth Removal