Recent Posts
Gingival Depigmentation (Gingival Bleaching)

Table of Contents
Gingival depigmentation, commonly referred to as gingival bleaching, is a cosmetic dental procedure aimed at removing or reducing melanin pigmentation in the gums. This pigmentation can lead to dark or black spots on the gingiva, which some individuals find aesthetically unpleasing. This procedure is particularly popular among patients seeking a uniform and lighter gum color to enhance the overall appearance of their smile.
Causes of Gingival Pigmentation
- Gingival pigmentation is primarily caused by an excess production of melanin, the pigment responsible for the color of our skin, hair, and eyes. Several factors can contribute to this condition:
Genetics: Melanin hyperpigmentation is often hereditary, more prevalent in individuals with darker skin tones. - Systemic Conditions: Certain systemic conditions like Addison’s disease can lead to increased melanin production.
- Medications: Some drugs, particularly certain antimalarials and antipsychotics, can cause pigmentation changes.
- Smoking: Nicotine can stimulate melanin production, leading to darker gums
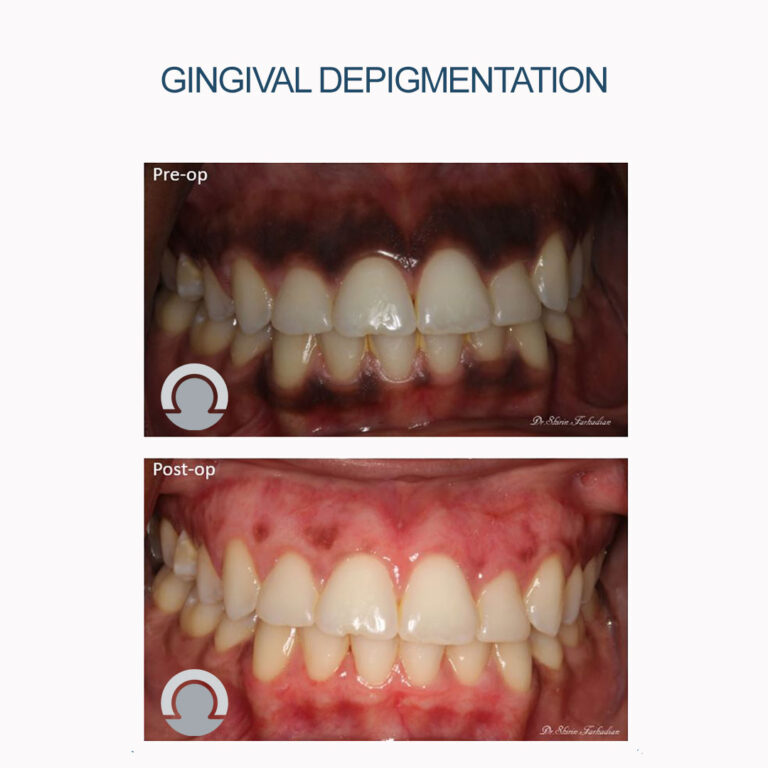
Techniques for Gingival Depigmentation
Several methods are used to achieve gingival depigmentation, each with its own benefits and potential drawbacks. The choice of method depends on the extent of pigmentation, patient preference, and the dentist’s expertise.
1. Scalpel Surgical Technique:
– Procedure: Involves removing the pigmented layer of the gingiva using a scalpel.
– Advantages: Cost-effective and does not require advanced equipment.
– Disadvantages: Can cause discomfort and bleeding, with a longer healing time.
2. Laser Ablation:
– Procedure: Utilizes laser energy to ablate the pigmented tissues.
– Advantages: Minimally invasive, less painful, minimal bleeding, and faster healing.
– Disadvantages: More expensive due to the need for specialized equipment.
3. Cryosurgery:
– Procedure: Involves freezing the pigmented tissues with a cryogen like liquid nitrogen.
– Advantages: Effective with minimal discomfort.
– Disadvantages: Risk of damage to surrounding tissues and potential for uneven results.
4. Electrosurgery:
– Procedure: Uses electric currents to remove pigmented tissue.
– Advantages: Controlled tissue removal with reduced bleeding.
– Disadvantages: Requires skill to avoid thermal damage to adjacent tissues.
5. Chemical Peeling:
– Procedure: Application of chemical agents like phenol or alcohol to peel off the pigmented layer.
– Advantages: Non-invasive and straightforward.
– Disadvantages: Can cause chemical burns and may require multiple sessions.
Post-Operative Care and Recovery
Post-operative care is crucial for optimal healing and preventing complications. Common post-operative recommendations include:
– Pain Management: Over-the-counter pain relievers or prescribed medications to manage discomfort.
– Oral Hygiene: Gentle brushing with a soft-bristle toothbrush and avoiding abrasive toothpaste.
– Dietary Adjustments: Soft, non-spicy foods to prevent irritation of the treated area.
– Follow-Up Visits: Regular check-ups to monitor healing and address any concerns.
Risks and Considerations
While gingival depigmentation is generally safe, it carries potential risks such as:
– Infection: Ensuring sterile conditions during the procedure minimizes this risk.
– Relapse: Pigmentation may recur, necessitating repeat procedures.
– Scarring: Rare but possible, particularly with surgical methods.
Conclusion
Gingival depigmentation is an effective cosmetic procedure for individuals seeking to improve the appearance of their gums. With advancements in dental technology, various methods offer patients options tailored to their needs and comfort levels. Consulting with a dental professional can help determine the most appropriate approach based on individual cases.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What is the primary cause of gingival pigmentation?
– Gingival pigmentation is mainly due to excessive melanin production, often influenced by genetic factors, systemic conditions, medications, and lifestyle choices like smoking.
2. Is gingival depigmentation a permanent solution?
– Results can be long-lasting, but pigmentation may recur over time, especially if the underlying cause is not addressed. Repeat treatments may be necessary.
3. How painful is the gingival depigmentation procedure?
– Pain levels vary depending on the method used. Laser and chemical techniques tend to be less painful, while surgical methods might cause more discomfort. Pain is generally manageable with medications.